Characterization of CO2 Storage Potential in Harquahala Basin, Arizona


Project Description
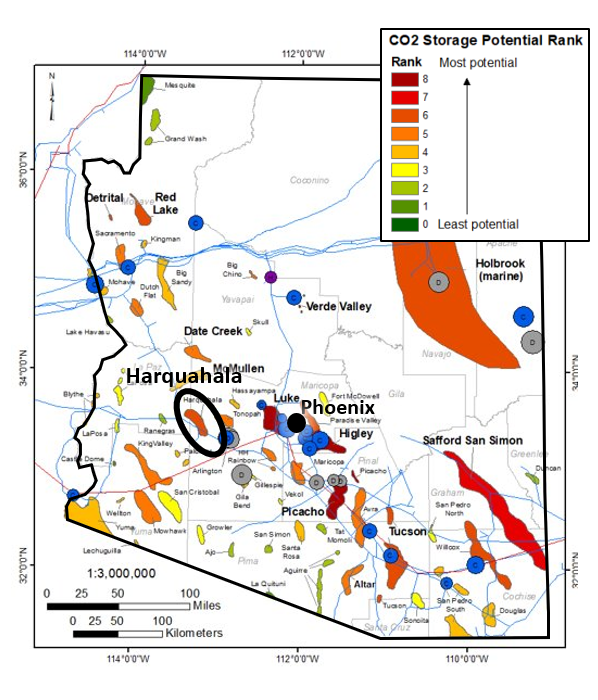
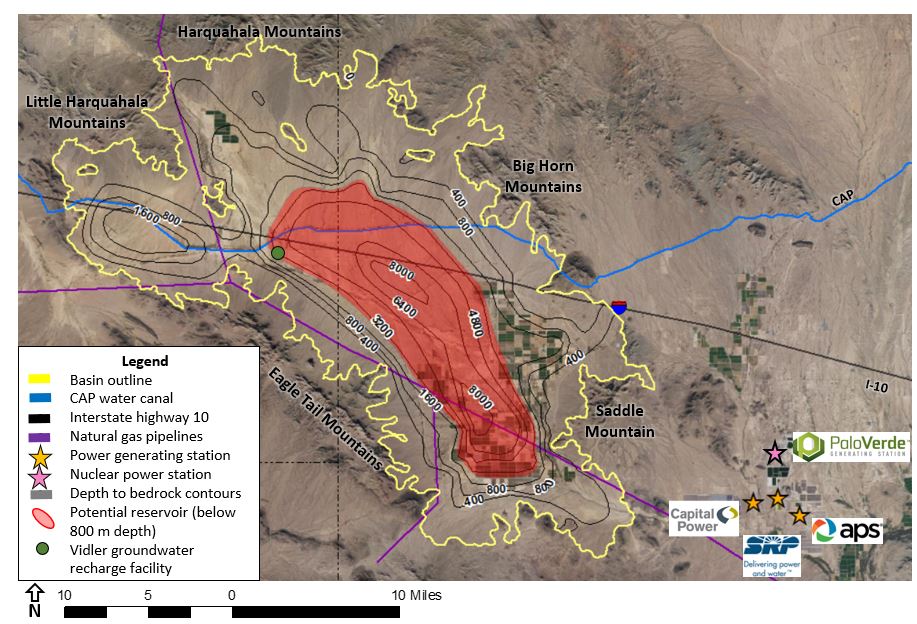
The Arizona Geological Survey (AZGS) is working to characterize CO2 storage potential in Harquahala basin, western central Arizona. The basin is favorably located between population centers of southern California and south-central Arizona, and is close to large energy producers and existing infrastructure. The basin is deep and possesses a mix of saline aquifers and basalt formations, providing sufficient volume to store large volumes of CO2. Also, the basin has probable bedded salt that could provide an adequate seal for hydrogen storage, giving yet another dimension to the project.
AZGS is collaborating with several partners including NIKOLA Motor Company, Salt River Project, Arizona Public Service and Tucson Electric Power. The main objective is to compile and integrate all existing data to deliver subsurface map products that highlight important reservoir characteristics, identify data gaps, and can be used to guide a future data acquisition program.
This project will provide needed data to the CUSP, and is intended to set the stage for a Phase 2 project where data acquisition such as geophysical surveys and a characterization well will be proposed.
CUSP Team
Project Lead: Briant Gootee (Arizona Geological Survey)
Primary Goal
Pre-feasibility evaluation for potential underground storage of CO2
Project Duration
24 months
Impact on Carbon Storage
Anticipated Volume/Year
Project Objectives
- Collect data, process seismic, create basin cross-sections and construct model layers for 3-D model development in Phase II
- Cultivate partnerships with energy companies
- Identify data needs and recommendations for Phase 2
- Update CUSP databases
- Publish Open-File Report
- Develop a Phase 2 project proposal with partners
Why Harquahala?
- Deep basin with sufficient volume
- Three potential geologic storage types:
-
- Hypersaline aquifer – liquid CO2
- Bedded salt – potential H2 storage
- Basalt – CO2 mineralization
-
- Potential large volume of saline groundwater
- Favorable geothermal potential
- Proximity to large energy producers
- Existing pipeline ROW between southern AZ and CA
- Low seismicity risk
Risks
- Unknown sealing potential
- Poor subsurface well control